Did you know your pineal gland is smaller than a pea but very important? It helps control your body's internal clock. This part of the brain is key to the endocrine system's work.
- Understanding the Pineal Gland: An Overview
- Location of the Pineal Gland in the Brain
- Detailed Pineal Gland Diagram and Anatomy
- The Pineal Gland's Connection to the Endocrine System
- Melatonin Production and Secretion Process
- Circadian Rhythm Regulation and Sleep Patterns
- The Third Eye Concept: Scientific Perspective
- Pineal Gland Calcification: Causes and Effects
- Natural Methods for Pineal Gland Decalcification
- Relationship Between the Pineal and Pituitary Glands
- Common Disorders Affecting the Pineal Gland
- The Role of the Pineal Gland in Spiritual Practices
- Modern Research and Scientific Discoveries
- Maintaining Optimal Pineal Gland Health
- Environmental Factors Affecting Pineal Function
- Conclusion
- FAQ - Frequent Asked Questions
The pineal gland is deep in the brain. It sends messages to keep your body's rhythms in sync. Its role is amazing, affecting sleep, hormone levels, and health balance.
Looking at the pineal gland diagram shows a complex part of our body. It makes melatonin, the hormone that controls when we sleep and wake. Scientists are learning more about how it affects our health.
Key Takeaways
- Pineal gland is a tiny but powerful endocrine organ
- Located deep within the brain's center
- Produces melatonin to regulate sleep patterns
- Critical component of the body's biological clock
- Plays a significant role in hormone regulation
Understanding the Pineal Gland: An Overview
The epiphysis cerebri, also known as the pineal gland, is a fascinating part of human anatomy. It has intrigued scientists and philosophers for centuries. This small gland plays a key role in our body's functions.
Historical Significance and Discovery
René Descartes first brought attention to the pineal gland in the 17th century. He saw it as a link between our physical body and spiritual mind. Today, scientists continue to study its unique role in the brain.
Basic Anatomical Features
The pineal gland's anatomy is quite interesting. It's shaped like a pine cone and is located in the brain's center. It measures:
- 5-8 millimeters in length
- 0.1-0.2 grams in weight
- It has a reddish-gray color
Role in Human Biology
The pineal gland is vital for regulating our body's rhythms. It produces melatonin, which controls our sleep-wake cycles. This gland responds to light and dark to keep our body's internal clock in sync.
“The pineal gland is nature's timekeeper, silently orchestrating your body's most fundamental rhythms.” – Neuroscience Research Journal
Learning about the pineal gland helps us understand how our body keeps its balance. It's a key part of our physiology.
Location of the Pineal Gland in the Brain
The pineal gland is in a special spot in the brain. It's deep in the brain's center, between the two halves. It's near the third ventricle and the corpus callosum.
Knowing where the pineal gland is shows its key role in brain work. This small, pine cone-shaped organ is almost in the brain's center. This lets it talk to many neural systems well.
- Precise anatomical location: Between the two cerebral hemispheres
- Proximity to critical brain structures
- Central positioning for optimal neural communication
“The pineal gland's central location makes it a fascinating nexus of neurological activity.” – Neuroscience Research Journal
The brain's layout helps the pineal gland get and use sensory info from many neural paths. Its spot lets it help control hormones and brain functions. This includes sleep and wake cycles.
Neuroanatomists find the pineal gland's spot very interesting. Its central place shows it has a big role. It connects different neural networks and is a key communication spot in the brain.
Detailed Pineal Gland Diagram and Anatomy
Exploring the pineal gland's anatomy is fascinating. It shows us a complex world of biology. Knowing its structure helps us understand its important role in our brains.
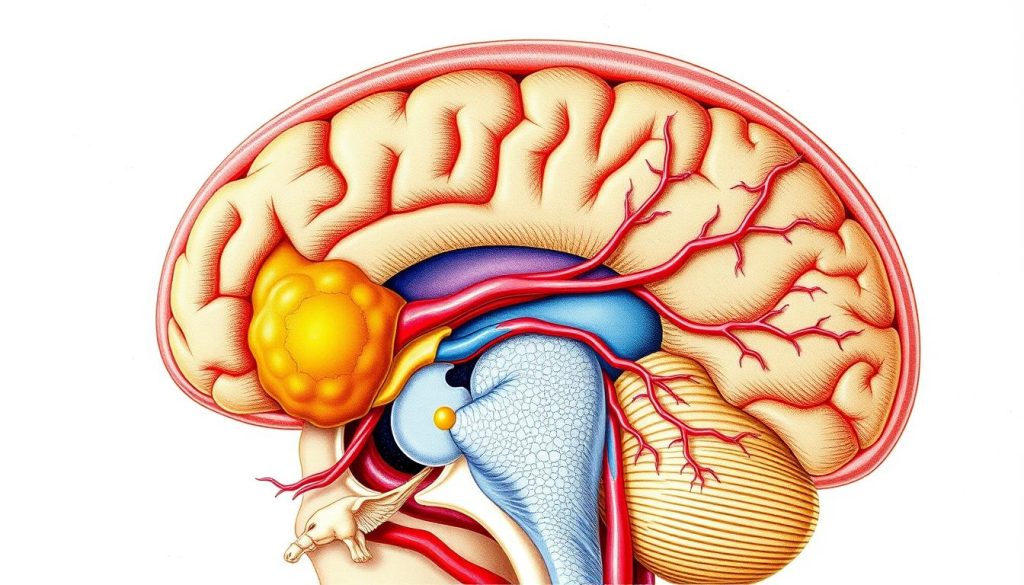
A detailed diagram of the pineal gland is key for doctors and scientists. This small gland is deep in the brain. It plays a big part in many body processes.
External Structure Overview
The pineal gland looks like a pinecone. This shape is why it's called that. It has:
- Approximate size of 5-8 millimeters
- Reddish-gray coloration
- Smooth, symmetrical surface
- Located in the epithalamic region
Internal Components
The pineal gland has special cells inside. These cells are key to its work. Inside, you'll find:
- Pinealocytes: Primary secretory cells
- Glial cells: Supporting neural tissue
- Interstitial spaces: Facilitate cellular communication
Blood Supply and Innervation
The pineal gland gets a lot of blood. This blood comes through special nerves. Its blood system helps it work well and make hormones.
| Blood Supply Source | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Posterior cerebral arteries | Primary blood delivery |
| Sympathetic nerve fibers | Neurological signaling |
| Parasympathetic connections | Regulatory mechanisms |
“The pineal gland represents a remarkable intersection of neurological and endocrine systems.” – Neuroscience Research Institute
Learning about the pineal gland's diagram is very important. Each part of it helps keep our body balanced. It supports our brain's functions.
The Pineal Gland's Connection to the Endocrine System
Your body's endocrine system is like a complex network. The pineal gland is a key player in this network. It's a small gland in the brain but plays a big role in many body functions.
The pineal gland is special in the endocrine system because of its unique abilities:
- It makes melatonin, a hormone that helps us sleep and wake up.
- It works with many hormonal pathways.
- It responds to light and dark signals from the environment.
- It helps control our body's internal clock.
Knowing how the pineal gland works with hormones shows its importance. It talks to other glands in the body. This helps control:
- How hormones for reproduction are made.
- How we handle stress.
- How our body uses energy.
- How our immune system works.
“The pineal gland is like a mystical conductor of your body's hormonal symphony” – Neuroendocrine Research Institute
Scientists are studying how the pineal gland works with the endocrine system. They're learning how it can affect our health and well-being.
| Endocrine Interaction | Primary Function | Impact on Body |
|---|---|---|
| Melatonin Secretion | Sleep Regulation | Manages Circadian Rhythms |
| Hormonal Signaling | Reproductive Coordination | Influences Sexual Maturation |
| Stress Response | Cortisol Modulation | Regulates Emotional Balance |
The pineal gland's amazing ability to work with many endocrine pathways shows its key role in keeping our body's hormonal balance.
Melatonin Production and Secretion Process
Your pineal gland is key in making melatonin. This hormone helps control your sleep and wake cycles. Knowing how it works can show you its vital role in your body's clock.
Synthesis Pathway of Melatonin
Melatonin starts with tryptophan, an amino acid. The pineal gland changes it into melatonin through several steps:
- Conversion of tryptophan to serotonin
- Enzymatic transformation of serotonin
- Final production of melatonin
Regulatory Mechanisms
The making of melatonin is controlled by light and brain signals. Light affects how much melatonin is made. Darkness makes more hormone.
| Regulatory Factor | Impact on Melatonin |
|---|---|
| Light Exposure | Suppresses Melatonin Production |
| Darkness | Stimulates Melatonin Secretion |
| Suprachiasmatic Nucleus | Synchronizes Circadian Rhythms |
Release Patterns
The pineal gland releases melatonin in a certain way. Melatonin levels go up in the evening, peak at night, and drop in the morning.
“Melatonin is nature's most sophisticated sleep regulator” – Sleep Research Experts
Learning about these processes can help you sleep better and keep your body's clock healthy.
Circadian Rhythm Regulation and Sleep Patterns
Your pineal gland is key in managing sleep and circadian rhythms. It's a small but mighty organ that acts as your body's clock. It controls when you feel awake or tired.
The pineal gland mainly makes melatonin, a hormone that tells your body it's time to sleep. When it gets dark, your pineal gland makes more melatonin. This gets you ready for bed.
“The pineal gland is nature's timekeeper, synchronizing our biological processes with environmental light cycles.”
Key Mechanisms of Sleep Regulation
- Melatonin production triggers sleep onset
- Light exposure directly impacts hormone secretion
- Maintains consistent sleep-wake cycles
Knowing how your pineal gland works can help you sleep better. Problems with your circadian rhythms can cause health issues like insomnia and metabolic problems.
| Circadian Rhythm Phase | Melatonin Level | Typical Time |
|---|---|---|
| Sleep Preparation | High | 9-10 PM |
| Deep Sleep | Peak | 2-4 AM |
| Waking Phase | Low | 6-8 AM |
By keeping healthy sleep habits and understanding your pineal gland, you can greatly improve your sleep and rhythm.
The Third Eye Concept: Scientific Perspective
The pineal gland third eye concept links ancient mysticism with modern science. Your brain has this amazing gland that has fascinated many for centuries.

The pineal gland's mystical connections tell a story of spiritual awakening and brain function. This small gland, shaped like a pine cone, is deep in your brain. It has caught the attention of people from different cultures.
Ancient Beliefs
Old civilizations saw the pineal gland as a spiritual center. They believed it had deep spiritual meaning. Here are some views from different cultures:
- Hindus thought it was the sixth chakra's place
- Egyptians linked it to divine consciousness
- Philosophers like René Descartes saw it as the soul's link
“The pineal gland is the seat of the soul” – René Descartes
Modern Scientific Understanding
Today, scientists have found out a lot about the pineal gland. They know it's key for making melatonin and controlling our body's clock.
| Ancient Perspective | Modern Scientific View |
|---|---|
| Spiritual gateway | Hormone-producing endocrine gland |
| Mystical consciousness center | Melatonin secretion regulator |
| Divine connection point | Neurological light-sensitivity mechanism |
Even though ancient views seem far from today's science, researchers keep looking into how our brain and consciousness are connected.
Pineal Gland Calcification: Causes and Effects
Pineal gland calcification happens as we age. It can affect our body's hormonal balance. Calcium builds up in the pineal gland, which can disrupt its function.
“The pineal gland's vulnerability to calcification highlights the importance of understanding its health mechanisms.” – Neuroscience Research Institute
Several factors lead to pineal gland calcification:
- Advanced age
- Chronic fluoride exposure
- High levels of environmental toxins
- Poor dietary habits
- Chronic stress
The effects of pineal gland calcification can be big. It might mess with melatonin production. This affects sleep and our body's internal clock.
| Calcification Stage | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Early Stage | Mild sleep disruption |
| Moderate Stage | Reduced melatonin production |
| Advanced Stage | Significant hormonal imbalances |
Knowing about pineal gland calcification lets us take care of our gland. Regular health checks and changes in our lifestyle can reduce risks.
Natural Methods for Pineal Gland Decalcification
Keeping your pineal gland healthy is vital for your brain and overall well-being. Decalcifying your pineal gland means removing mineral deposits that slow it down. Natural methods can help your pineal gland work better and support its important functions.

Dietary Approaches to Support Decalcification
Your diet is key to a healthy pineal gland. Some foods can help remove calcification and aid in detoxification.
- Eat organic, raw fruits and vegetables
- Drink more citrus fruits for antioxidants
- Choose foods rich in chlorophyll
- Avoid processed foods and artificial additives
Lifestyle Changes for Optimal Pineal Gland Function
Changing your lifestyle can help decalcify your pineal gland and improve brain health.
- Limit fluoride in water and toothpaste
- Practice meditation and stress reduction
- Get better sleep and keep regular hours
- Use electronic devices less, before bed
Supplementation Options
| Supplement | Potential Benefits | Recommended Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| Iodine | Supports detoxification | 150-300 mcg daily |
| Boron | Reduces calcium buildup | 3-6 mg daily |
| Apple Cider Vinegar | Helps dissolve calcium deposits | 1-2 tablespoons daily |
“The pineal gland is your body's internal compass, and keeping it clear can unlock remarkable healing and awareness.” – Dr. Andrew Weil
Remember, decalcifying your pineal gland takes time. Stick to your plan and be patient. This will help your body heal naturally.
Relationship Between the Pineal and Pituitary Glands
The pituitary and pineal glands are key parts of the endocrine system. They work together to control many body functions. These glands talk to each other through hormones, affecting sleep and metabolism.
Here's what's interesting about the pineal and pituitary glands:
- They are both in the brain's center.
- They share messages through nerves and hormones.
- Each has its own role in keeping the body balanced.
The pituitary gland is like the “master gland.” It helps control hormone levels in the body. It also affects the pineal gland's melatonin, which helps you sleep. This shows how the endocrine system works together.
“The pineal and pituitary glands represent a remarkable example of biological synchronization and neural communication.” – Dr. Elizabeth Rodriguez, Neuroendocrinology Researcher
Your body's hormones depend on these two glands working together. The pituitary gland sends signals that change the pineal gland's melatonin. This affects your sleep and body balance.
Scientists are studying how these glands work together. They are learning more about how they help keep your body's hormonal system in check.
Common Disorders Affecting the Pineal Gland
The pineal gland is vital for our body's rhythms. But, like any organ, it can face disorders. Knowing about these issues helps you spot health problems early and get the right care.
Many medical conditions can harm the pineal gland's work. These problems might come from genes, the environment, or other health issues.
Primary Symptoms of Pineal Gland Disorders
- Irregular sleep patterns
- Hormonal imbalances
- Neurological disruptions
- Circadian rhythm disturbances
Diagnostic Approaches
Doctors use special tests to find pineal gland problems. These include:
- Neuroimaging scans
- Hormone level testing
- Comprehensive neurological examinations
| Disorder Type | Primary Symptoms | Diagnostic Method |
|---|---|---|
| Pineal Calcification | Sleep disruption | CT Scan |
| Melatonin Dysfunction | Hormonal irregularities | Blood Test |
| Tumor Development | Neurological symptoms | MRI Screening |
Treatment Options
Treatment for pineal gland issues depends on the problem and its cause. Your doctor might suggest:
- Medication to regulate hormone production
- Surgical intervention for tumors
- Lifestyle modifications
- Targeted therapeutic interventions
“Early detection and a thorough medical check-up are essential for managing pineal gland disorders well.” – Neurology Research Institute
Always talk to a qualified doctor for advice on pineal gland health and disorders.
The Role of the Pineal Gland in Spiritual Practices
The pineal gland has long fascinated spiritual seekers and researchers. It's often called the third eye. This tiny brain structure connects science and spirituality. Your journey into understanding the pineal gland's mystical connections begins here.

Ancient traditions see the pineal gland as a powerful center for spiritual awakening. Cultures worldwide have called it a gateway to higher consciousness. Yogic and meditative practices aim to activate the third eye for spiritual growth.
“The pineal gland is our direct connection to spiritual realms, a biological antenna for cosmic consciousness.” – Spiritual Neuroscience Research
- Connects biological processes with spiritual experiences
- Considered a key energy center in metaphysical traditions
- Potential mechanism for intuitive and transcendent states
Scientific research shows the pineal gland makes dimethyltryptamine (DMT). This compound is linked to deep mystical experiences. Activating the pineal gland through meditation can boost spiritual perception and inner awareness.
Understanding the pineal gland's role in consciousness expansion supports your spiritual journey. By exploring practices that nourish and decalcify the pineal gland, you may reach deeper spiritual awareness.
Modern Research and Scientific Discoveries
The pineal gland is a mystery that scientists are eager to solve. They are studying its complex functions and how it can help us. Recent studies have given us new insights into this organ's role in our health.
Recent Breakthrough Studies
Scientists have found out a lot about the pineal gland. They've learned about its role in our brain and body. Some key discoveries include:
- Neurotransmitter regulation and brain function
- Advanced neuroplasticity mechanisms
- Potential neuroprotective capabilities
- Intricate hormonal communication networks
Emerging Research Directions
New research is looking into exciting areas:
- Neurological disorder interventions Scientists are exploring how the pineal gland can help with diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
- Advanced neuroimaging techniques New imaging tools are giving us a closer look at the pineal gland's structure and how it works.
- Genetic mapping Genetic studies are finding connections between the pineal gland and certain health issues.
“The pineal gland represents a frontier of neurological understanding, promising new insights into complex biological interactions.” – Dr. Elena Rodriguez, Neuroscience Research Institute
As research keeps growing, the pineal gland stays a key area of study. It holds the promise of new treatments and a deeper understanding of our biology.
Maintaining Optimal Pineal Gland Health
Your pineal gland is key for sleep and wellness. To keep it healthy, you need a balanced approach. This supports melatonin production and fights off environmental stress.
Here are some ways to help your pineal gland:
- Minimize exposure to blue light before bedtime
- Practice stress reduction techniques like meditation
- Ensure consistent sleep schedules
- Consume antioxidant-rich foods
What you eat affects melatonin production. Add these foods to your diet for better pineal gland health:
- Chlorella – supports detoxification
- Dark leafy greens
- Raw cacao
- Apple cider vinegar
“The quality of your sleep depends on the health of your pineal gland.” – Holistic Health Experts
Exercise regularly and keep your environment clean. This helps avoid pineal gland calcification. Avoid fluoride, processed foods, and too much electromagnetic radiation for better health.
Everyone is different. Talking to a healthcare professional can help tailor advice for your pineal gland and overall health.
Environmental Factors Affecting Pineal Function
Your pineal gland is key to keeping your body's clock in sync. Things around us can mess with this delicate system. This can throw off your sleep and wake times.

Light is a big player in how well your pineal gland works. Too much artificial light, like from screens, can mess with your sleep hormones. This can mess up your natural rhythm.
- Electromagnetic fields from electronic devices
- Persistent urban light pollution
- Chemical toxins in the environment
- Chronic stress and lifestyle factors
Recent studies point out a few big environmental challenges for your pineal gland:
- Electromagnetic Radiation: Too much WiFi, mobile signals, and gadgets might change how your pineal gland works
- Chemical Pollutants: Toxins in the air can harden your pineal gland. This makes it less effective at making hormones
- Stress Environments: Ongoing stress can lower melatonin levels
“The pineal gland serves as a sensitive environmental sensor, responding to subtle changes in our surroundings.” – Neuroscience Research Institute
Knowing how our environment affects our pineal gland can help. It's about keeping your sleep patterns in check and your body in balance.
Conclusion
Your exploration of the pineal gland diagram shows us a world of biological complexity. This small gland is key to many body functions, like sleep and hormone balance. It's a powerful communicator in our body.
Science keeps finding out more about the pineal gland. It's involved in melatonin production and might link to our body's rhythms and spiritual feelings. Knowing about it helps us take care of our health.
As studies go on, the pineal gland's role gets more interesting. Taking care of it through diet and lifestyle can boost our health. Learning about this gland helps us understand our bodies better and find new ways to stay healthy.
The pineal gland shows us how complex our bodies are. It reminds us that even small parts are very important. Knowing about it helps us understand the balance in our bodies.
FAQ – Frequent Asked Questions
What is the pineal gland?
The pineal gland is a small gland in the brain, known as the “third eye.” It makes melatonin, which helps you sleep and wake up. This tiny gland is key to your body's health and timing.
Where is the pineal gland located in the brain?
The pineal gland is deep in the brain, in the epithalamus area. It's about the size of a grain of rice. It's near important brain parts, making it vital for your body's health.
What is the primary function of the pineal gland?
The pineal gland's main job is to make melatonin. This hormone helps you sleep and wake up. It makes more melatonin when it's dark and less when it's light.
What is pineal gland calcification?
Pineal gland calcification is when calcium builds up in the gland. This can lower melatonin and mess with your sleep. It happens more with age and can be affected by diet and environment.
How does the pineal gland affect sleep?
The pineal gland affects sleep by making melatonin. When it gets dark, it makes more melatonin. This makes you sleepy and helps keep your sleep cycle regular.
Can lifestyle choices impact pineal gland function?
Yes, your lifestyle can affect your pineal gland. Avoiding blue light before bed, sleeping at the same time every day, and reducing fluoride can help. Also, stress reduction and dark sleep areas are important.
Is there a connection between the pineal gland and spirituality?
Many believe the pineal gland is the “third eye” for spiritual awareness. While science doesn't fully back this, its role in the brain and hormone production has sparked interest in spirituality.
How can I support my pineal gland health?
To keep your pineal gland healthy, try these: sleep at the same time every day, avoid artificial light at night, and reduce stress. Eat foods full of antioxidants, drink plenty of water, and limit fluoride and calcium supplements.